Proper nutrition is the cornerstone of a healthy life, influencing everything from energy levels and cognitive function to disease prevention and longevity. Understanding your daily nutritional needs is crucial for maintaining bodily functions, enhancing mental well-being, and preventing chronic diseases. In today’s fast-paced world, people often prioritize convenience over well-being, leading to nutritional imbalances that can significantly impact health and overall quality of life.
By comprehensively understanding essential nutrients—macronutrients like carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, along with vital micronutrients such as vitamins and minerals—you can create a sustainable dietary plan that promotes longevity and vitality. Nutrition affects every system in the body, including metabolic health, immune resilience, and even mental clarity.
This guide provides an in-depth look into daily nutrition requirements, detailing not only the foundational aspects of nutrient intake but also the latest scientific recommendations and practical strategies to integrate balanced nutrition into your lifestyle. Whether you are looking to improve your diet, optimize athletic performance, manage weight, or prevent chronic conditions, understanding and implementing proper nutrition is key to long-term well-being.
What Are Daily Nutrition Requirements?
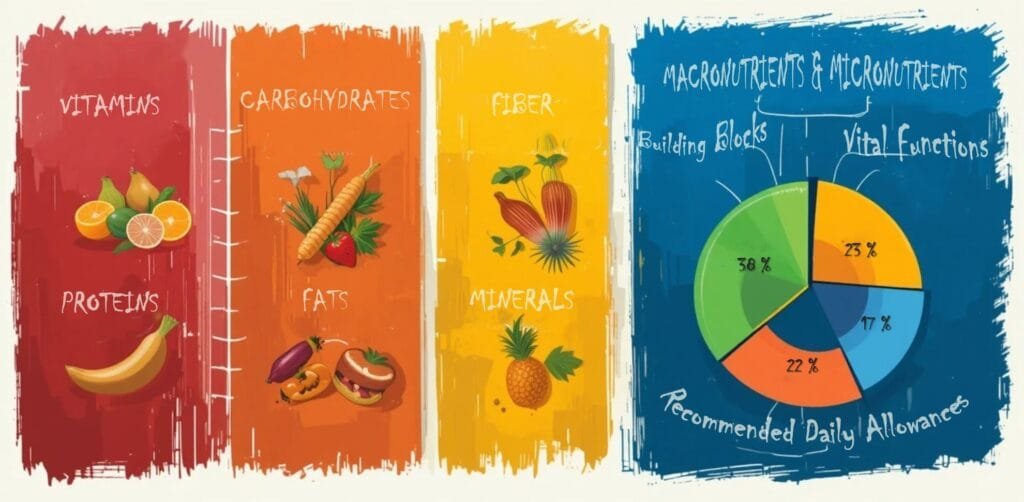
Daily nutrition requirements refer to the specific amounts of essential nutrients needed to support the body’s physiological functions. These nutrients include macronutrients (carbohydrates, proteins, and fats) and micronutrients (vitamins and minerals), each playing a vital role in maintaining overall health.
Types of Nutrients
Macronutrients: The Building Blocks of Health
- Carbohydrates – The body’s primary energy source, essential for brain function and physical activity. Found in whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes, carbohydrates provide the fuel needed for daily activities and metabolic processes. Complex carbohydrates, such as those found in quinoa, oats, and sweet potatoes, offer sustained energy release and help stabilize blood sugar levels, preventing energy crashes. Fiber-rich sources like beans and lentils also aid digestion and promote gut health.
- Proteins – Crucial for tissue repair, muscle growth, enzyme production, and immune function. Proteins are derived from sources like lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy, legumes, nuts, and seeds. High-quality proteins, such as those from wild-caught fish and organic poultry, provide essential amino acids necessary for muscle repair and neurotransmitter function. Plant-based protein sources like lentils, chickpeas, and tofu contribute to satiety and cardiovascular health.

- Fats – Necessary for absorbing fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K), protecting organs, and providing long-term energy. Healthy fats from sources such as avocados, nuts, olive oil, and fatty fish support brain function and cardiovascular health. Omega-3 fatty acids found in flaxseeds, walnuts, and salmon are particularly beneficial for reducing inflammation and enhancing cognitive performance. Monounsaturated fats from olives and almonds help regulate cholesterol levels and support heart health.
Micronutrients: Essential for Vital Functions
- Vitamins – Organic compounds required in small amounts for various bodily functions, including immune health, energy production, and bone strength. Key vitamins include:
- Vitamin A (vision, immune function) – Found in carrots, sweet potatoes, and dairy. Supports eye health, cellular communication, and immune defense.
- Vitamin C (antioxidant, skin health) – Found in citrus fruits, bell peppers, and strawberries. Enhances collagen synthesis, promotes wound healing, and boosts immunity.
- Vitamin D (bone health, immune support) – Found in sunlight exposure, fortified dairy, and fatty fish. Crucial for calcium absorption, bone density, and mood regulation.
- Vitamin E (antioxidant, skin protection) – Found in nuts, seeds, and vegetable oils. Helps combat oxidative stress and supports cardiovascular health.
- Vitamin K (blood clotting, bone health) – Found in leafy greens, broccoli, and fermented foods. Plays a role in blood coagulation and maintaining bone mineral density.
- Minerals – Inorganic elements like calcium, potassium, and iron, essential for bone health, fluid balance, and oxygen transport.
- Calcium (bone strength) – Found in dairy, leafy greens, and fortified plant-based milks. Essential for bone mineralization, nerve function, and muscle contraction.
- Iron (oxygen transport) – Found in red meat, beans, lentils, and spinach. Supports hemoglobin production and prevents anemia.
- Magnesium (muscle and nerve function) – Found in nuts, seeds, and whole grains. Vital for muscle relaxation, heart rhythm regulation, and energy production.
- Potassium (fluid balance, heart health) – Found in bananas, potatoes, and legumes. Helps maintain blood pressure, electrolyte balance, and nerve signaling.
- Zinc (immune system, wound healing) – Found in shellfish, pumpkin seeds, and chickpeas. Essential for immune defense, tissue repair, and enzyme function.
Understanding Recommended Daily Allowances (RDAs)
Recommended Daily Allowances (RDAs) are scientifically established guidelines formulated by health organizations to specify the average daily intake levels necessary to meet the nutrient requirements of the majority of healthy individuals. These recommendations take into account various physiological factors such as age, biological sex, and distinct life stages, including pregnancy, lactation, and advanced age, to ensure that individuals receive adequate nutrition for optimal health. RDAs play a critical role in the prevention of nutrient deficiencies and associated health conditions, serving as a foundation for dietary planning and nutritional policies worldwide. These guidelines are periodically updated based on emerging scientific research to reflect advancements in our understanding of human nutrition and metabolic health. Proper adherence to RDAs supports overall well-being, enhances immune function, maintains metabolic efficiency, and reduces the risk of chronic diseases such as osteoporosis, cardiovascular disorders, and diabetes.

Why Are Daily Nutrition Requirements Important?
1. Supporting Vital Bodily Functions
Every nutrient plays a specific role in maintaining bodily functions. Carbohydrates fuel the brain and muscles, proteins repair tissues, and fats support hormone production and cell structure. A well-balanced intake of these nutrients ensures optimal functioning and reduces the risk of deficiencies.
2. Preventing Chronic Diseases
A diet rich in essential nutrients helps lower the risk of chronic diseases such as:
- Heart Disease – By maintaining healthy cholesterol levels and blood pressure through a diet high in fiber, healthy fats, and antioxidants.
- Diabetes – By stabilizing blood sugar levels with whole grains, lean proteins, and fiber-rich foods.
- Osteoporosis – By ensuring adequate calcium and vitamin D intake for strong bones.

3. Enhancing Physical and Mental Well-being
- Cognitive Function – Nutrients like omega-3 fatty acids and B vitamins improve brain health, reducing the risk of neurodegenerative diseases.
- Emotional Stability – Magnesium and vitamin D play a role in mood regulation, helping prevent depression and anxiety.
- Energy Production – Iron, vitamin B12, and complex carbohydrates sustain energy levels throughout the day.
4. Maintaining a Healthy Weight
Balancing macronutrient intake prevents overeating and supports metabolism, making it easier to maintain a healthy weight. Proper nutrition reduces cravings and promotes satiety, leading to better portion control and healthier food choices.
Conclusion
Meeting your daily nutrition requirements is fundamental to sustaining overall health, preventing chronic illnesses, and optimizing both physical and cognitive performance. A well-balanced diet, combined with adequate hydration and mindful eating, not only enhances energy levels but also fortifies the immune system, supports digestive efficiency, and maintains emotional stability. By implementing a nutrient-dense eating regimen, individuals can improve metabolic function, regulate hormone production, and strengthen cardiovascular health. Whether adopting minor dietary modifications or undertaking a comprehensive nutritional transformation, prioritizing wholesome food choices contributes to long-term vitality and longevity. The path to optimal health begins with informed decisions—embrace mindful eating today and lay the foundation for a healthier, more fulfilling future.